- March 17, 2025
- Posted by: Velosi Author
- Categories: Asset Integrity, Insights

Introduction to Risk Based Inspection
Efficient Risk Based Inspection methodology can reduce unexpected breakdowns, and equipment malfunctions can have an impact on how smoothly operations run and the profits they yield. Risk based inspection (RBI) is now seen as a strategy that assists businesses in making the most of their inspection resources while safeguarding asset reliability and safety. By focusing on inspections according to risk evaluations, organizations can cut down on maintenance expenses and avert breakdowns. Prolong the lifespan of their equipment.
Velosi strategically directs inspection efforts to areas, for results. The result? Clients save big on maintenance costs and boost equipment reliability and uptime.
What is Risk-Based Inspection?
Risk-based inspection (RBI) is a methodology that prioritizes inspection activities based on the risk associated with mainly static equipment failure. Unlike traditional time-based inspection approaches, which apply the same inspection frequency to all assets regardless of their condition or criticality, RBI allocates resources according to where they’re needed most.
API RP 580: A Risk Assessment and Management process is focused on the loss of containment of pressurized equipment in processing facilities, due to material deterioration. These risks are managed primarily through equipment inspection.
The core principle of RBI is simple yet powerful: focus inspection efforts on high-risk static equipment while reducing unnecessary inspections of low-risk assets. This approach not only optimizes resources but also enhances safety and reliability.
Consequence of Failure (COF) × Probability of Failure (POF) = Risk
Static machinery in refining, petrochemical, chemical process, and oil and gas production facilities comprises pressurized permanent equipment including pressure vessels, pipelines, tankage, pressure relief devices (PRDs), and heat exchanger tube bundles.
It also defines risk as the sum of the probability of failure (POF) and the consequence of failure (COF). Failure is thus defined as a loss of containment from the pressure boundary, which results in leaking into the atmosphere or the rupture of a pressurized component.
For risk-based inspection, we identify and manage relative risk. We recognize that we do not always have access to the absolute numbers required to predict with 100 percent accuracy. However, when our models optimize or become more precise, we better understand the uncertainties and have more tools to reduce the ambiguity in our predictions.

RBI Standards and Methodologies
Several established standards guide RBI implementation:
- API 580/581: American Petroleum Institute’s framework for RBI programs
- ASME PCC-3: American Society of Mechanical Engineers’ inspection planning guidelines
- DNV-RP-G101: Det Norske Veritas’ recommended practice for RBI
- EN 16991: European standard for risk-based inspection framework
Business Overview
What sets Velosi’s approach apart is its integration of industry standards like API 580/581 and ASME with proprietary assessment tools developed through decades of field experience. This rounded approach guarantees adherence, to regulations. Delivers practical and economical solutions customized to fit the specific operational conditions of each facility.
“Our approach to risk assessment at Velosi extends beyond crunching numbers,” the team at Velosi elaborates. ” We blend analysis with hands-on experience to create inspection strategies that tackle issues encountered in industrial sites.”
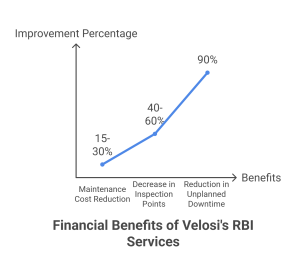
The financial benefits of implementing Velosi’s RBI services are compelling. Clients typically report:
- 15-30% reduction in overall maintenance costs
- 40-60% decrease in inspection points without compromising safety
- Extension of equipment lifecycles by 3-5 years
- Up to 90% reduction in unplanned downtime
- Significant improvements in maintenance resource utilization
Key Benefits of Implementing Risk Based Inspection
- Reduction in Unplanned Downtime
- Optimized Maintenance Costs
- Extended Equipment Life
- Enhanced Safety and Compliance
The Risk Based Inspection Implementation Process
Implementing an effective Risk Based Inspection program typically involves these essential steps:
- Data Collection and Equipment Categorization
The initial phase entails collecting information on every piece of machinery such, as design specifications, operational settings, maintenance records and reasons, for malfunction. The equipment is then classified according to its purpose the materials its made of and the conditions under which it operates.
- Risk Assessment
Risk is calculated as a combination of the probability of failure and the consequence of failure. This assessment considers factors such as:
– Damage mechanisms (corrosion, erosion, fatigue)
– Operating environment
– Equipment age and condition
– Historical inspection data
– Consequence of failure (safety, environmental, financial)
- Inspection Planning
Based on the risk assessment, inspection plans are developed that specify:
– Inspection techniques (visual, ultrasonic, radiographic)
– Inspection locations
– Inspection intervals
– Required resources and expertise
- Implementation and Monitoring
Once the inspection plan is implemented, the results are documented and used to update the risk assessment. This creates a continuous improvement cycle that refines the RBI program over time.
Velosi’s Comprehensive RBI Methodology
Velosi’s RBI implementation follows a systematic, proven methodology:
- Initial Assessment: Evaluate the risks by estimating the likelihood and impact of failure, for each piece of equipment using Velosis customized risk assessment tools that take into account factors such, as operating conditions and material characteristics.
- Risk Analysis: Calculate probability and consequence factors for each equipment item using Velosi’s specialized risk matrices, which consider process conditions, material properties, and potential failure mechanisms.
- Inspection Planning: Development of optimized inspection plans that specify techniques, locations, intervals, and resource requirements based on risk profiles.
- Implementation Support: Expert guidance during the execution of inspection plans, including technician training, procedure development, and quality assurance.
- Continuous Improvement: Ongoing analysis of inspection results to refine risk assessments and further optimize maintenance activities over time.
This structured approach ensures consistent results across diverse facility types and operating environments.
Prioritize, Redefine Asset Integrity with our extensive VAIL-Plant® ® Modules
Innovative RBI implementation supports competitive VAIL-Plant®® Modules
- PEMS (Pressurized Equipment Management System): A comprehensive solution for managing pressurized equipment.
- PIMS (Pipelines Integrity Management System- Onshore & Offshore): A robust system designed for both onshore and offshore pipeline integrity management.
- CIMS (Civil Integrity Management System): An advanced system to analyze, assess, and inspect civil natures like Concrete Structures, Pipe Sleeper, Flare, Water Well, Fencing, Culverts, Foundations, Roads & Paving, Buildings, and Pipe Track Foundations, etc.
- SIMS (Structural Integrity Management System): Systematically designed module for securing compliance with regulatory and organizational requirements. We endorse international codes, such as ISO 19900, ISO 19902, ISO 19904, and API RP 2 SIM, for our structural integrity experts to ensure the sustainability and integrity of onshore and offshore structures.
- HIMS (Hull Integrity Management System): A fully customized system that focuses on a rationalized methodology to perform inspections of Hull structures.
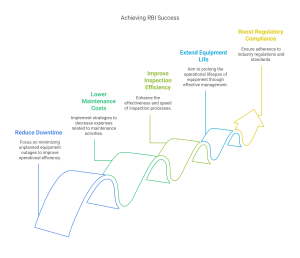
Measuring RBI Success
The effectiveness of an RBI program can be measured through several key performance indicators:
– Reduction in unplanned downtime
– Decrease in maintenance costs
– Improved inspection efficiency
– Extended equipment life
– Enhanced regulatory compliance
Organizations typically see the best results when Risk Based Inspection is integrated into their overall asset integrity management strategy and supported by strong leadership commitment.
Conclusion
To conclude, Risk-Based Inspection methodology is employed by process industries for the management of asset integrity. With increasing operating problems and reduced profit margins, the conventional time-based inspection method is inadequate to provide the efficiency and reliability that today’s facilities demand.
Velosi’s Risk-Based Inspection service offers a comprehensive solution that shifts maintenance strategies from reactive to proactive, from calendar-based to risk-informed methodologies, and from resource-based to best-efficiency operations.
The data-driven, risk-informed future of industrial maintenance involves allocating resources where they deliver the most value. Risk-Based Inspection is at the forefront, delivering a proven system for balancing the conflicting cost, compliance, and reliability demands.
Moreover, with focused technical expertise, established methodologies, and uncompromising commitment to quantifiable outcomes, Velosi remains at the forefront of risk-based inspection practice development within the international process industry.
Stay connected for more blogs!
Please contact us for more information and assistance.