RBI to CMP Transformation
- April 25, 2022
- Posted by: Velosi Author
- Categories: Asset Integrity, Insights

RBI TO CMP TRANSFORMATION
The oil and gas, process industries handle a broad variety of potentially dangerous combustible and poisonous chemicals. To keep risks to a manageable level, authorities have enforced obligations on plant and facility management via law, forcing them to show that they have recognized existing hazards and implemented required inspection and mitigation steps to avoid accidents.
Due to the cyclical analysis of the organization, operators are continuously forced to strike a compromise between regulatory compliance and minimizing business disruption. Plants that improve their efficiency and reliability will be better positioned for long-term survival and success.
Furthermore, to accomplish these objectives, new asset integrity methods such as RBI and CMP are increasingly being used. RBI aims to ensure safe and cost-effective integrity management of containment systems on the plant, maximizing availability and production regularity while ensuring personnel safety, ensuring an efficient transfer of experience between disciplines and locations and serves as a tool for continuous improvement.
What is Risk-Based Inspection (RBI)?
Risk-based inspection (RBI) is described as a risk-based analysis for assessing loss of containment circumstances, considering that risk is controlled through inspection activities or inspection plans. Besides, the primary objective of an RBI study is to identify high-risk equipment and piping, to concentrate inspection resources, it may be used as a risk management tool, due to its consistency and simple approach for risk assessment. It applies to both offshore and onshore facilities, including permanent or mobile units, FPSOs, and pipelines.
Realistic Engineering facilities cannot be developed or run on the premise of “zero risks.” But, by using Risk-Based Inspection, it is feasible to maintain or decrease to acceptable levels (RBI).
Risk is defined as the “probability of failing x consequence of failure”.
By implementing an effective RBI program, reduced risks may be accomplished while maintaining the same level of inspection activity, which is both cost and time-effective. The following figure-1 illustrates this idea following API 580:
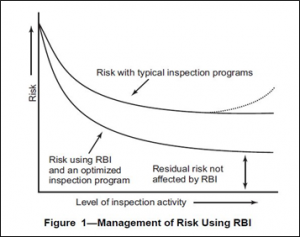
What is CMP?
Corrosion management programs (CMP) are integrated tools that have been designed to detect asset performance and maximize plant dependability and utilization while maintaining a high standard of safety and environmental sustainability. A well-designed Corrosion Management Program is the most useful material to promote corrosion knowledge management, corrosion talent development and training, and integration with other disciplines such as process, operation, inspection, and maintenance.
Formulated objectives off CMP include:
- Reducing the number of corrosion-related hydrocarbon releases, as well as other potentially hazardous and environmentally damaging outcomes.
- Identifying best practices for implementing an effective corrosion management plan.
- Providing an overview of the top corrosion threats to downstream production and processing facilities.
What distinguishes CMP from RBI?
CMP (Corrosion Management Program) is a conceptual plan that includes methods for reducing and managing the risk associated with various plants.
The corrosion control document is the primary output of this program. It details the corrosion control and mitigation methods required to prevent the corrosion and failure of a plant’s integrity and dependability.
Recently, the oil and gas industry has opted for a Corrosion Management Program (CMP) over a Risk Assessment Program, as this program encompasses not only the risk associated with assets, but also policies, processes, and procedures that address corrosion throughout the asset lifecycle, from design to withdrawing.
What Elements are included in the Corrosion Management Program?
The key elements for the corrosion management program are the following:
- Identification of Corrosion Threats
- Major Historical Corrosion challenges
- Risk-Assessment
- Work Processes (Core, Strategic, Tactical, Elemental, and Atomic)
- Corrosion Control and mitigation Strategies
- Corrosion Monitoring and Inspection
- Integrity Operating Windows
- Program Performance Review and Management
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Reviews and Continuous Improvement
Work process analysis in CMP offers opportunities for future document and work process gaps in the facility, as well as an active decision to reduce these gaps, putting the facility on a path of continuous improvement.
The CMP approach combines based on emerging and developed technologies that affect proactive corrosion management processes such as corrosion monitoring (chemical injection, fluid sampling, coupons), corrosion protection (lining, cladding, coating), corrosion prediction (software), life assessment, material selection, and statistical analysis, among others.
RBI assessment is an element of CMP, which produces a risk analysis and inspection plan that, when implemented, may effectively manage asset risk while saving significant money and time.
As part of the CMP, IOWs (Integrity Operating Windows) are created that concentrate on mechanical or chemical variables that affect corrosion/material deterioration, such as metal temperature, velocity, differential pressure, pH, and contaminant or corroding concentrations.
Each Integrated Operating Windows (IOW) outlines minimum and maximum values, measurement frequency and urgency, the repercussions of deviations, potential underlying causes of deviations, and corrective measures needed to restore equilibrium.
This integrity operating window (IOW) enables plant/operations staff to monitor for and correct any deviations, which adds value to the asset’s life. Additionally, this corrosion prevention technique assists in preventing impending damage at an early stage, rather than waiting for inspection services to detect issues after a certain time, which may become serious, if left untreated for an extended period.
CMP offers engineers and management a defined process (CMP Dashboard) that allocates responsibility for meeting key performance indicators (KPIs), reviewing corrosion-related operations on a regular basis, and implementing corrosion control and mitigation actions for the facility. Corrosion is a cost of conducting business that must be handled if optimum advantage is to be obtained.
Corrosion management program is used in the oil and gas industry because it not only addresses risk factors but also offers recommendations for the smooth and continuous operation of plants at maximum output.
The corrosion management (CM) process, if implemented early in the design process, has the potential to significantly improve asset corrosion mitigation post-commissioning. However, several prerequisites must be met in order to properly implement the corrosion management process across a project. Human resources, competency, teamwork, and managerial support are examples of these.
Conclusion
Corrosion management for any oil and gas asset (or any part or system thereof) could be defined as the process of reviewing the required integrity management measures, regular monitoring of their performance, and post-commissioning evaluation of their effectiveness.
The term ‘the required integrity management measures’ in this definition encompasses design, material selection, corrosion mitigation, inspection, corrosion monitoring, management, and Failure Risk Assessment (FRA).
Please contact us for more information and assistance.



